- cascade of sequential activation converts each proenzymes into its active state and amplifies the response.
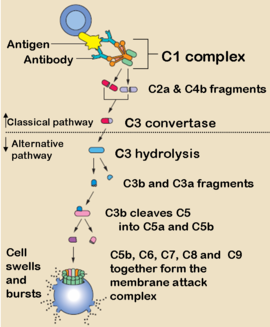
Classical pathway
- triggered by IgM or IgG (antigen-antibody complex)
- C1 is the initiating protein, after binding to Fc able to activate C2 and C4, which in turns activate C3
Alternative pathway
- initiated by certain antigens (lipopolysaccharides, endotoxin) and IgA complexes on cell surface which activates C3
C3 is activated by classical and altenative pathways
Lectin pathway
- mannose binding lectin (MBL) is a collectin that is able to bind through its lectin proteins on carbohydrates present on bacteria which indirectly activates next complement C2 and C4
inherited deficiencies
- C1 inhibitor deficiencies - hereditary angioneurotic edema (uncontrolled complement activation)
- C2, C4 deficiencies - HSP, SLE, glomerulonephritis, streptococcal infection
- C5-C9 deficiencies - Neisserial infection

No comments:
Post a Comment