- medium-size vessel
vasculitis
- usually in
middle aged men
- associated with
hepatitis B antigenaemia (10-20%)
- pathology: fibrinoid necrosis of vessels walls with microaneurysm formation, thrombosis and infarction
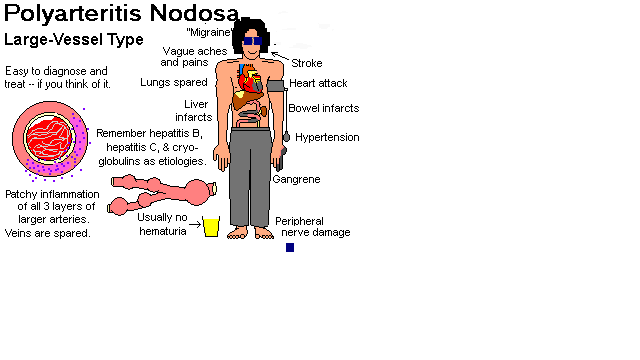
- presents with fever, malaise, weight loss, myalgia,
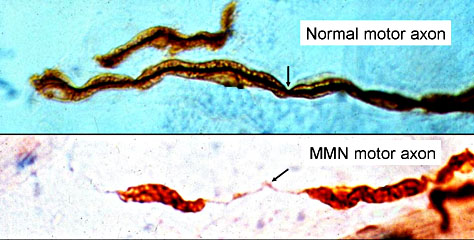
mononeuritis multiplex (arteritis of vasa nervorum),
livedo reticularis, abdominal pain,
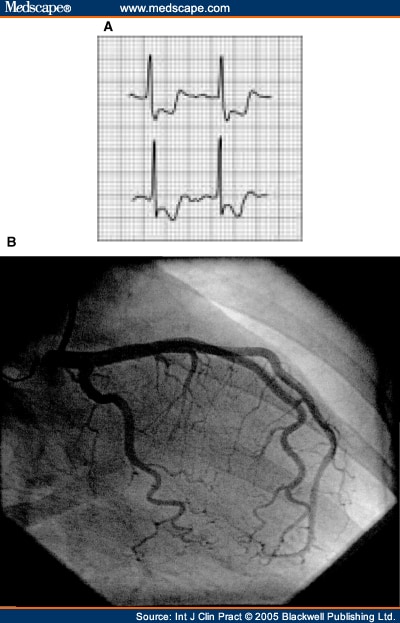
hematuria/proteinuria, hypertension, myocardial infarction,
subcutaneous hemorrhage/gangrene
- P-ANCA
negative, rarely involved lungs (differentiate from Churg Strauss)
- investigations:
raised ESR,
elevated creatinine, anemia, leukocytosis, microaneurysm in angiography
- treatment: steroids, azathioprine
ACR Criteria for the Classification of Polyarteritis Nodosa (PAN)
American College of Rheumatology 1990 criteria for the classification of polyarteritis nodosa (PAN). Classified as PAN if at least three of the 10 criteria are present:
- Weight loss > 4 kg: Loss of >4 kg body weight since illness began, not related to dieting or other factors.
- Livedo reticularis: Mottled reticular pattern over the skin of portions of the extremities or torso.
- Testicular pain/tenderness: Pain or tenderness of the testicles, not due to infection, trauma or other causes.
- Myalgias, weakness or leg tenderness: Diffuse myalgias (excluding shoulder or hip girdle) or weakness of muscles or tenderness of leg muscles.
- Mono- or polyneuropathy: Development of mononeuropathy, multiple mononeuropathies orpolyneuropathy.
- Diastolic BP >90 mmHg: Development of hypertension with the diastolic BP higher than 90 mmHg.
- Elevated BUN or creatinine: Elevation of BUN >40 mg/dl or creatinine >1.5 mg/dl, not due to dehydration or obstruction.
- Hepatitis B virus: Presence of hepatitis B surface antigen or antibody in serum.
- Arteriographic abnormality: Arteriogram showing aneurysms or occlusions of the visceral arteries, not due to arteriosclerosis, fibromuscular dysplasia or other non-inflammatory causes.
- Biopsy of small or medium-sized artery containing polymorphonuclear cells: Histologic changes showing the presence of granulocytes or granulocytes and mononuclear leucocytes in the artery wall.
These criteria have a reported sensitivity of 82.2% and a reported specificity of 86.6% for the classification of polyarteritis nodosa compared with other vasculitides.