- G6PD oxidises glucose-6-phosphate to 6-phosphogluconolactone with reduction of NADP to NADPH. Thus G6PD is to protect red cell from oxidative damage
- On exposure to infection, fava beans, certain drugs, patient will develop intravascular hemolysis with hemoglobinuria
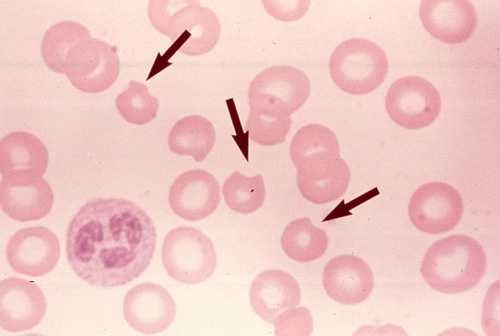
- Blood film : bite cells (degmacytes), blister cells with Heinz bodies (oxidized denature hemoglobin) removed by spleen
- Treatment: stop the offending drug, maintain a high urine output and transfuse if necessary
in female if the child is G6PD def but mother is carrier, father normal then what is d possible reason for her to be G6PD def le?
ReplyDeleteG6PD deficieny is X-linked recessive disorder, thus commoner in male.In such condition, lyonisation (random inactivation of X-chromosome in female) would be the reason for manifestation in female.
ReplyDelete